Hoses Used on Bucket Trucks
HOSES USED ON BUCKET TRUCKS

Hoses used on bucket trucks must be capable of handling frequent movement and abrasion, the bucket is constantly moving up and down, causing the hoses to abrade against the trucks boom arms. This persistent friction can wear through a hose’s cover and lead to failure. Bucket truck hoses also tend to run at high pressure, so your hose will need to be rated to the appropriate PSI. Don’t hesitate to reach out to the Pros at TCH for the proper hose for your job!
WHAT HOSE IS USED FOR BUCKET TRUCKS?
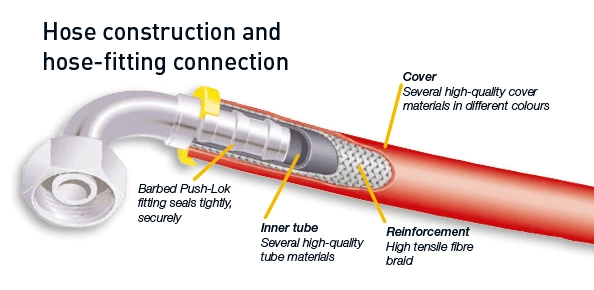
As mentioned with pressure ratings, hydraulic hose is always used on bucket truck lifts. A rubber hose would get the job done when it comes to pressure, but there are some other considerations that steer us away from using a standard, rubber hydraulic hose.
Because the lifts are intended for lifting a worker, for safety factors you always want to use a non-conductive hose. This will, as its name states, prevent the hose from conducting electricity to the worker in the boom. As the boom raises and lowers, it is constantly rubbing against the boom arms, causing damage to the cover over time; utilizing a thermoplastic hose–with its smooth cover–will help prevent this abrasion damage.
Take a look at Danfoss’ Synflex line to see exactly what we’re talking about. You can also learn how to select the right hydraulic hose in our blog post.
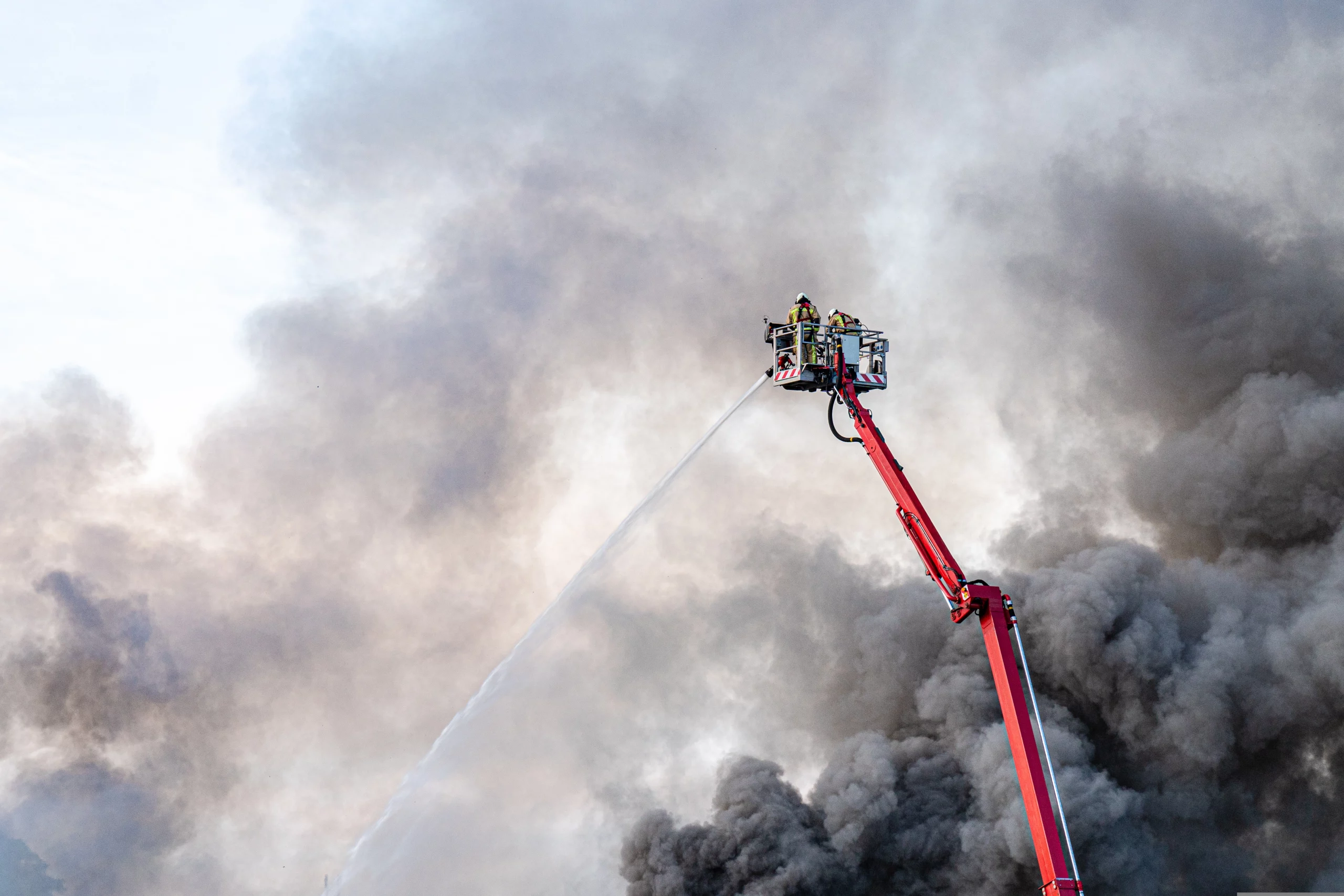
WHAT DOES BUCKET TRUCK MEAN?
In the simplest of terms, a bucket truck is a truck that is equipped with an extendable arm used for raising and lowering a worker.
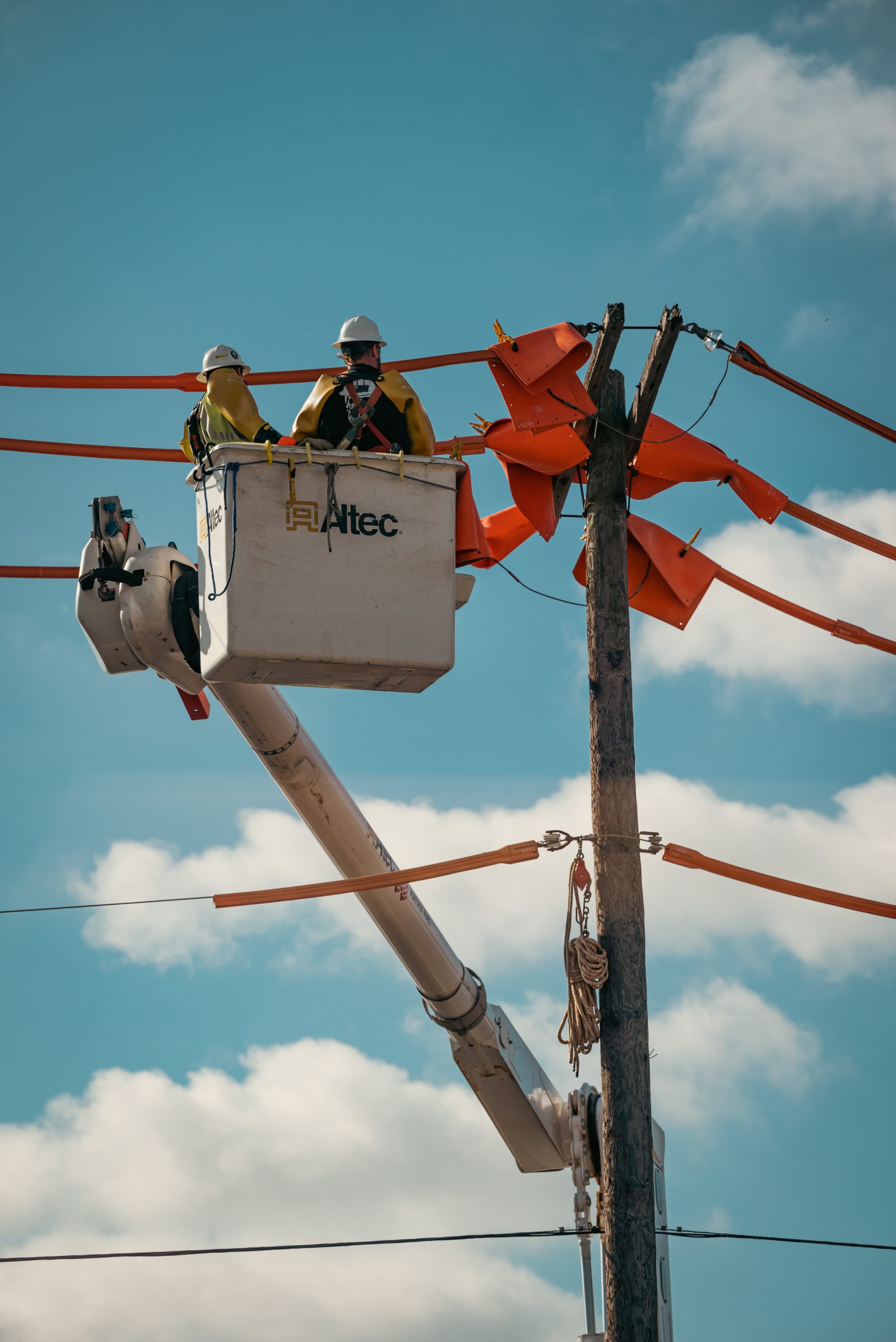
WHAT CAN A BUCKET TRUCK BE USED FOR?
These trucks are used in a variety of different applications:
- Electric Work/Telephone Lines
- Sign Maintenance
- Construction
- Landscaping
- Fire/Rescue
- Painting
- Window Washing

WHAT KIND OF HYDRAULIC FLUID GOES IN A BUCKET TRUCK?
At TCH Industries, we stock two types of hydraulic oil: ISO32 and ISO46.
ISO32
- Ideal for use in high-powered machine tools. For use in cooler weather; like an excavator during Fall, Winter, early, Spring.
- Low Viscosity Index: 32°F to °95F
- Ambient Temperature Range: -10°F to 85°F
- Viscosity @ 104°F is 30 mm2/s
- Viscosity @ 212°F is 5.3 mm2/s
- Viscosity Index: 100
- Flash Point COC: 401°F
- Pour Point: -22°F
- Density @ 59°F: 875 kg/m3
ISO42
- Normally required for industrial plants working under high-pressure etc. For use in warmer weather or in a plant with higher temperatures; like in an excavator during the Summer or in a press pump in a plant.
- Medium Viscosity Index: 95°F to 176°F
- Ambient Temperature Range: 10°F to 110°F
- Viscosity @ 104°F is 45 mm2/s
- Viscosity @ 212°F is 6.8 mm2/s
- Flash Point COC: 414°F
- Pour Point: -17°F
- Density @ 59°F: 880 kg/m3
WHAT IS THE BUCKET ON A BUCKET TRUCK CALLED?
Bucket trucks, as their name states, are known for their bucket lift, which is also referred to as a boom. These vehicles are highly sought after in many industries for their ease of use and ability to extend to heights that would otherwise be inaccessible.

We Are Hosers.
Our focus and obsession is the distribution, fabrication, and manufacturing of hose assemblies for industry and hose related products. Founded nearly 40 years ago, we are proudly owned and operated by the same family. Our manufacturing partners are some of the biggest and best names: Eaton, Parker, Dixon Valve, Hose Master, Brennan, Hannay Reels, and many others.
In short, we are a customer-centric hose company filled with happy professionals who can help you meet all your hose related needs.